Lupus in Dogs: Understanding and Managing the Condition
Introduction to Lupus Lupus is a complex immune-mediated disease where the immune system mistakenly attacks the body’s own DNA. This term originates from ancient beliefs attributing the condition to a wolf bite.
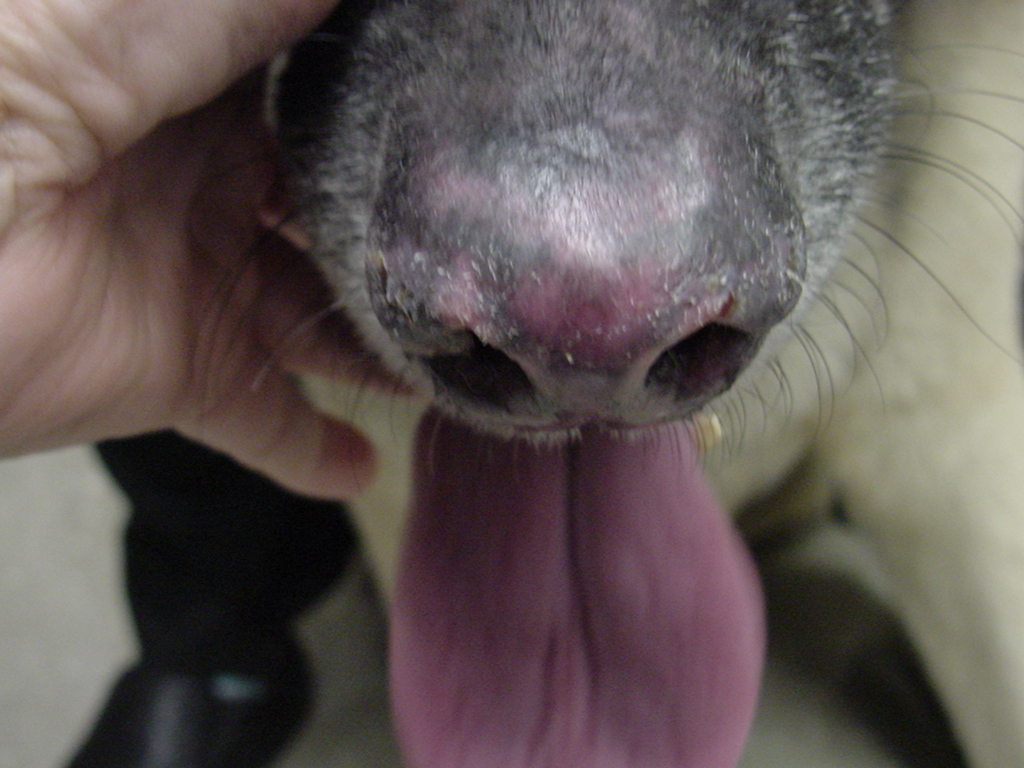
Types of Lupus in Dogs There are two primary forms of lupus in dogs: Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE) and Discoid Lupus Erythematosus (DLE). SLE is a more severe condition involving a Type III hypersensitivity reaction that can affect multiple organs. In contrast, DLE primarily affects the skin, particularly the nasal planum, and does not progress beyond the skin.
Diagnosing Lupus Lupus is diagnosed through the detection of antibodies generated by the immune system, which can deposit in various tissues such as joints and skin, leading to symptoms.
Managing Discoid Lupus
Conventional Therapy
-
Sun Protection: Intense sunlight can exacerbate symptoms, so it’s crucial to avoid strong sunlight. While sunscreens are commonly suggested, it’s important to use products that are safe for dogs, as they will likely ingest any substance applied to their nose.
-
Medications:
- Tetracycline and Niacinamide: This combination has been found to help about 70% of dogs with DLE and is typically administered three times daily.
- Prednisone/Prednisolone: These oral steroids can quickly bring the condition under control, with ongoing adjustments to find the lowest effective maintenance dose.
- 0.1% Tacrolimus (Protopic): A topical treatment that is safe for dogs even if licked, which makes it a viable option for treating DLE.
Alternative Treatments
- Tattooing the Nose: As an alternative to sunscreen, tattooing the nose can provide permanent protection against UV rays.
- Natural Remedies:
- Licorice Root Tincture: Can be used as a natural corticosteroid, administered orally or mixed with coconut oil for topical application.
- Omega 3 Fatty Acids: These supplements can reduce inflammation and are recommended for dogs with autoimmune diseases.
- Cannabidiol (CBD): Targeting the CB2 receptors, CBD has shown potential benefits in managing autoimmune diseases and can be used orally or topically.
The Role of the Endocannabinoid System (ECS) The ECS is integral in regulating immune response, inflammation, and other physiological processes. CBD interacts with the ECS, potentially helping to modulate and suppress an overactive immune response in dogs with lupus.
This comprehensive approach to managing lupus in dogs highlights both traditional and innovative therapies that can help improve their quality of life.